Cerebral Correlates and Statistical Criteria of Cross-Modal Face and Voice Integration
Résumé
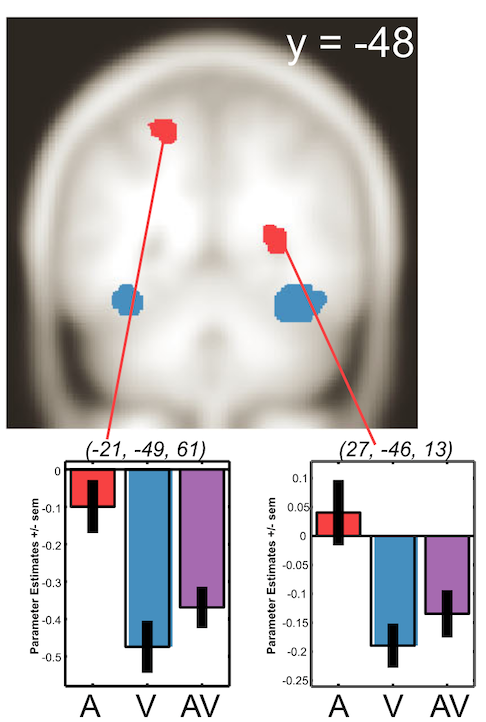
Perception of faces and voices plays a prominent role in human social interaction, making multisensory integration of cross-modal speech a topic of great interest in cognitive neuroscience. How to define potential sites of multisensory integration using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is currently under debate, with three statistical criteria frequently used (e.g., super-additive, max and mean criteria). In the present fMRI study, 20 participants were scanned in a block design under three stimulus conditions: dynamic unimodal face, unimodal voice and bimodal face–voice. Using this single dataset, we examine all these statistical criteria in an attempt to define loci of face–voice integration. While the super-additive and mean criteria essentially revealed regions in which one of the unimodal responses was a deactivation, the max criterion appeared stringent and only highlighted the left hippocampus as a potential site of face– voice integration. Psychophysiological interaction analysis showed that connectivity between occipital and temporal cortices increased during bimodal compared to unimodal conditions. We concluded that, when investigating multisensory integration with fMRI, all these criteria should be used in conjunction with manipulation of stimulus signal-to-noise ratio and/or cross-modal congruency.